Global Foreign Exchange (ForEx) Market Outlook to 2030
Region:Global
Author(s):Paribhasha Tiwari
Product Code:KROD6918
November 2024
86
About the Report
Global ForEx Market Overview
- The global Foreign Exchange (ForEx) market is valued at USD 800 billion in daily trading volume, driven by the high demand for currency exchange as international trade and cross-border investment continue to expand. The major drivers of this market include international businesses, central bank interventions, and the rising use of digital platforms for retail and institutional trading. The growing trend of algorithmic trading, which makes it easier for traders to capitalize on currency fluctuations, has also contributed to the consistent volume growth of the market.
- Key financial hubs, including New York, London, Tokyo, and Singapore, dominate the global ForEx market. New Yorks dominance is rooted in the role of the U.S. dollar, which accounts for the majority of all transactions as the global reserve currency. Similarly, London maintains a dominant position due to its strategic time zone, enabling it to serve both the U.S. and Asian markets. These cities also benefit from strong financial infrastructures and regulatory frameworks, making them attractive to institutional and retail traders alike.
- Several countries are accelerating their efforts to introduce CBDCs. In 2024, China's digital yuan accounted for $982 billion in forex transactions, facilitating faster cross-border trade settlements. Similarly, the European Central Bank (ECB) plans to introduce the digital euro by 2026, aiming to streamline eurozone cross-border transactions, which will impact the global forex market.
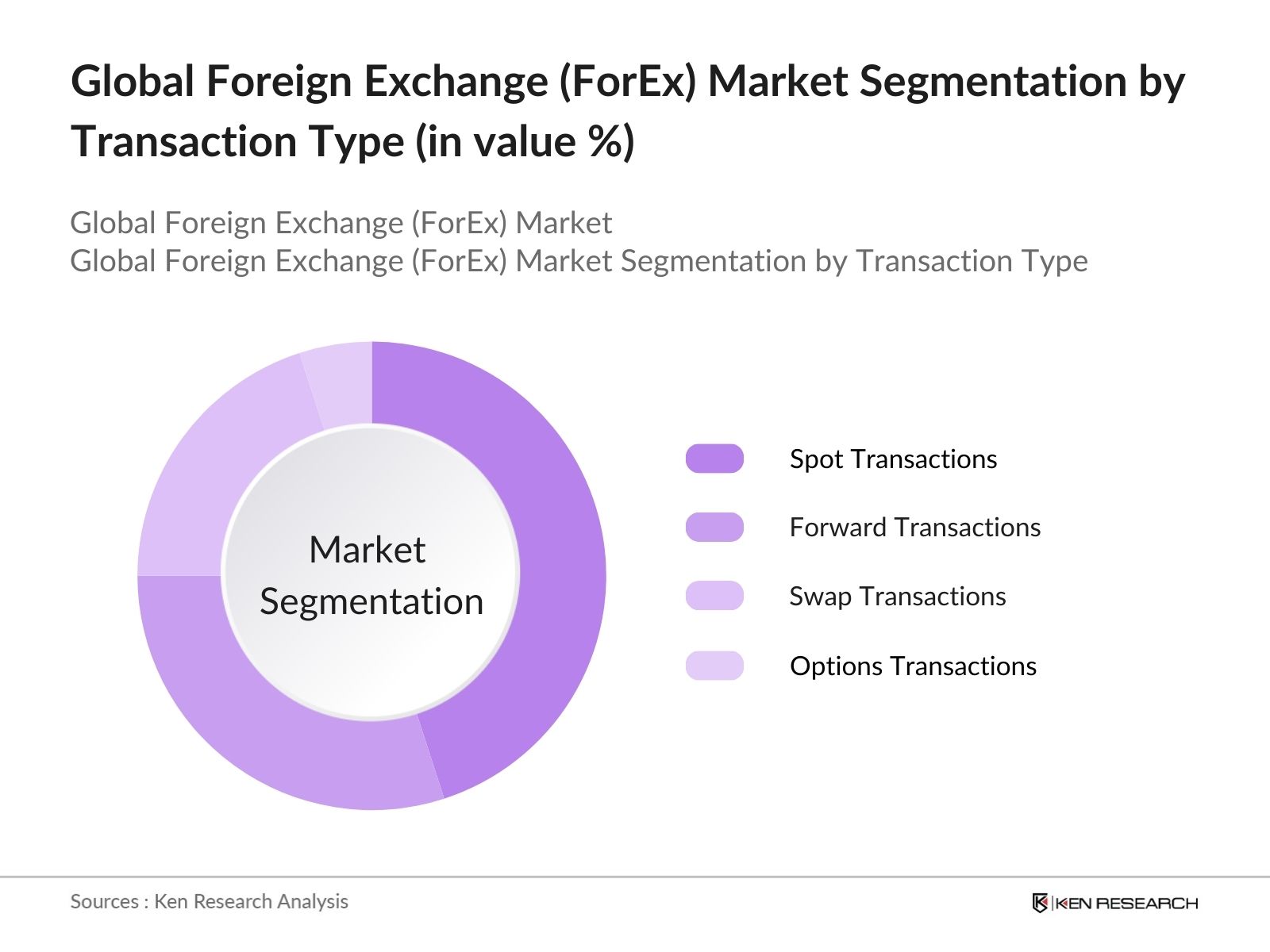
Global ForEx Market Segmentation
By Transaction Type: The global ForEx market is segmented by transaction type into Spot Transactions, Forward Transactions, Swap Transactions, and Options Transactions. Spot Transactions dominate the transaction type segment due to their real-time settlement feature, which is highly valued in fast-moving financial environments. Spot transactions are used by corporations and institutional investors to settle trades quickly, reducing the risk of currency fluctuation over longer time periods. The increasing volume of international trade and the rise in cross-border payments also contribute to the dominance of spot transactions. Furthermore, spot transactions are simpler and more liquid compared to forward or options transactions, making them the preferred choice for traders and institutions alike.
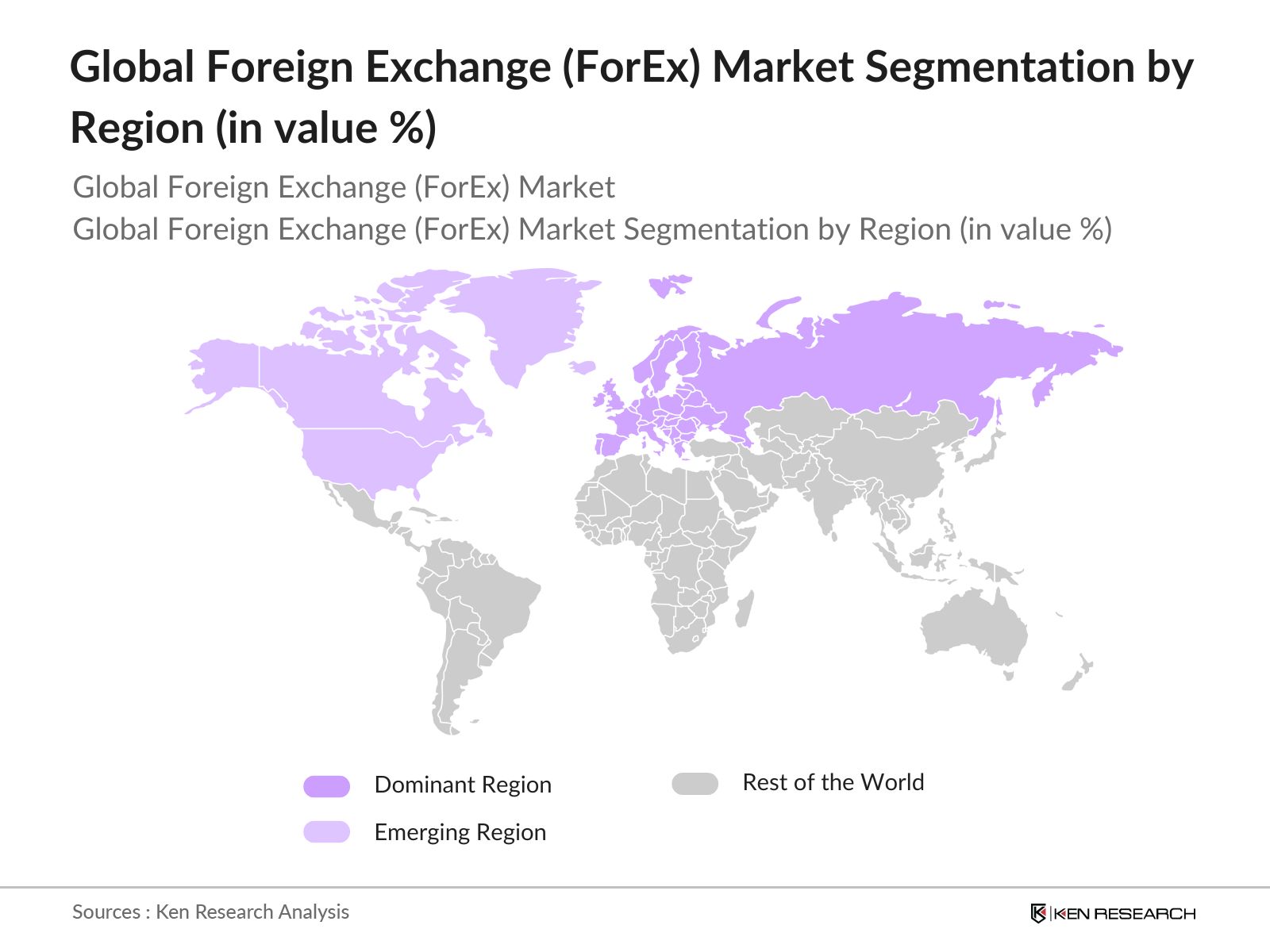
By Region: The global ForEx market is segmented by region into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America. Europe leads this segmentation due to the dominant role of London as a global financial hub. Londons time zone allows it to overlap with both U.S. and Asian trading hours, creating high liquidity throughout the day. Furthermore, Londons historical significance as a center for banking and finance, coupled with its robust financial regulatory framework, attracts a large volume of foreign exchange trading. The presence of major financial institutions and trading platforms also strengthens Europes leadership in the market.
By Participant Type: The ForEx market is also segmented by participant type, which includes Commercial Banks, Central Banks, Hedge Funds, and Retail Traders. Commercial Banks hold the largest market share under this segmentation because they act as intermediaries in the majority of foreign exchange transactions, providing liquidity to the market. Commercial banks also engage in proprietary trading and facilitate currency exchange for large-scale corporations. Their ability to leverage substantial capital, along with their extensive global networks, allows them to dominate this segment. The presence of strong trading platforms within these institutions further reinforces their leadership in the market.
Global ForEx Market Competitive Landscape
The global ForEx market is characterized by the dominance of major financial institutions and trading platforms. The largest players in the market, such as JPMorgan Chase and Citibank, leverage their vast networks and technological infrastructure to capture a significant portion of the market share. The consolidation of market power in these institutions highlights the influence they have over global currency transactions, and their continued innovation in algorithmic and high-frequency trading further strengthens their position.
|
Company Name |
Established |
Headquarters |
Trading Volume |
Trading Platforms |
Currency Pairs |
Algorithmic Trading |
Market Presence |
Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
JPMorgan Chase |
1799 |
New York, USA |
||||||
|
Citibank |
1812 |
New York, USA |
||||||
|
Deutsche Bank |
1870 |
Frankfurt, Germany |
||||||
|
UBS Group |
1862 |
Zurich, Switzerland |
||||||
|
HSBC |
1865 |
London, UK |
Global ForEx Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
- Algorithmic Trading, High-Frequency Trading: Algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading (HFT) have significantly increased market efficiency. As of 2024, the daily turnover in the global forex market is approximately $7 trillion, with over half of this volume driven by algorithmic and high-frequency trading platforms. This increased activity, especially in major hubs like New York, London, and Tokyo, boosts liquidity, reduces trade execution time, and increases accuracy in currency pricing.
- Import/Export Trade Data, International Remittances: Global trade continues to grow, especially in regions like Asia-Pacific and Europe. In 2023, global import-export trade reached $26 trillion, up by $3 trillion compared to pre-pandemic levels. Increased trade, especially between countries with high demand for commodities, has led to higher foreign exchange trading as businesses require currency conversion for transactions. Additionally, remittances from developed to developing countries stood at $630 billion in 2024, fueling more forex exchanges.
- Foreign Direct Investment, Portfolio Investments: In 2024, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows globally are projected to cross $1.5 trillion. Countries like the USA, China, and India attract significant FDI, resulting in increased forex demand as investors need to convert currencies to invest. Portfolio investments also contribute, with institutional investors requiring cross-border currency exchanges for global asset allocation. The increase in cross-border capital flows drives higher forex trading volumes.
Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Risks, Monetary Policy Changes: The ongoing geopolitical tensions, such as the Ukraine-Russia conflict and China-Taiwan relations, have led to significant fluctuations in major currencies like the Euro, Dollar, and Yuan. In 2024, the ruble, for example, lost nearly $30 billion in value due to sanctions, causing market instability. Additionally, changes in monetary policies by central banks (e.g., Federal Reserve rate hikes) contribute to unpredictable currency movements, affecting traders and investors globally.
- Capital Control Measures, Financial Conduct Regulations: Countries like China and India impose strict capital control measures, restricting the flow of foreign currencies. In 2024, India's Reserve Bank imposed a $20 million limit on capital outflows per individual annually, creating barriers for forex traders and investors. Additionally, new regulations by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) have increased compliance costs for forex brokers, hindering market growth.
Global ForEx Market Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the global ForEx market is expected to experience sustained growth, driven by advancements in trading technologies and the increasing participation of retail traders in the market. The rise of mobile trading applications, along with the expansion of algorithmic and high-frequency trading, is likely to further boost the markets trading volume. Additionally, the adoption of blockchain technology for secure and transparent transactions will play a key role in shaping the future of the market.
Market Opportunities
- Expansion of Emerging Market Currencies Emerging markets like India, Brazil, and South Africa are seeing increased participation in forex trading, with their currencies becoming more prominent in international trade. In 2024, the Indian rupee and Brazilian real collectively accounted for $300 billion in daily trade volume, with more institutions adding these currencies to their portfolios. This opens up new opportunities for investors looking to diversify and capitalize on growth in developing markets.
- Adoption of Blockchain for Settlement (Digital Currencies, Decentralized Finance) Blockchain technology is revolutionizing forex settlement processes by reducing transaction times and costs. In 2024, the global forex market saw nearly $500 billion in trades settled via blockchain technology. Digital currencies like the e-CNY (Chinese digital yuan) are gaining traction, as China processed over $180 billion worth of cross-border transactions using its digital currency, showcasing the potential for blockchain to streamline global payments.
Scope of the Report
|
By Transaction Type |
Spot Transactions Forward Transactions Swap Transactions Options Transactions |
|
By Participant Type |
Commercial Banks Central Banks Hedge Funds Retail Traders |
|
By Currency Pair Type |
Major Currency Pairs Minor Currency Pairs Exotic Currency Pairs |
|
By Trading Platform |
Traditional Bank Platforms Online Brokers Mobile Trading Apps |
|
By Region |
North America Europe Asia-Pacific Middle East & Africa Latin America |
Products
Key Target Audience
Institutional Investors and Traders
Hedge Funds
Central Banks
Commercial Banks
Foreign Direct Investment Firms
Retail Traders
Venture Capitalist Firms
Government and Regulatory Bodies (Bank for International Settlements, Financial Conduct Authority)
Companies
Players Mentioned in the Report:
JPMorgan Chase
Citibank
Deutsche Bank
UBS Group
HSBC
Barclays
XTX Markets
Goldman Sachs
BNP Paribas
Morgan Stanley
Table of Contents
1. Global ForEx Market Overview
1.1. Definition and Scope
1.2. Market Taxonomy
1.3. Market Growth Rate (Currency Pairs, Spot Market, Forward Market, Futures Market, Swaps)
1.4. Market Segmentation Overview
2. Global ForEx Market Size (In USD Trillion)
2.1. Historical Market Size (Spot Market, Forward Market, Futures Market, Options Market)
2.2. Year-On-Year Growth Analysis (Trading Volumes, Key Currency Pairs, Major Market Centers)
2.3. Key Market Developments and Milestones
3. Global ForEx Market Analysis
3.1. Growth Drivers
3.1.1. Technological Advancements (Algorithmic Trading, High-Frequency Trading)
3.1.2. Global Trade Growth (Import/Export Trade Data, International Remittances)
3.1.3. Investment Flows (Foreign Direct Investment, Portfolio Investments)
3.1.4. Rising E-commerce and Cross-Border Payments
3.2. Market Challenges
3.2.1. Currency Volatility (Geopolitical Risks, Monetary Policy Changes)
3.2.2. Regulatory Scrutiny (Capital Control Measures, Financial Conduct Regulations)
3.2.3. Cybersecurity Risks (Digital Trading Platforms, Payment Gateways)
3.3. Opportunities
3.3.1. Expansion of Emerging Market Currencies
3.3.2. Adoption of Blockchain for Settlement (Digital Currencies, Decentralized Finance)
3.3.3. Increased Participation of Retail Traders
3.4. Trends
3.4.1. Rising Use of Mobile and AI-based Trading Platforms
3.4.2. Growth in Cryptocurrency and Digital Assets Trading
3.4.3. Increased Algorithmic Trading Volume in Major Market Centers
3.5. Government Regulation
3.5.1. Basel III Compliance and Capital Requirements
3.5.2. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Policies
3.5.3. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Requirements
3.5.4. Financial Markets Infrastructure Regulation
3.6. SWOT Analysis
3.7. Stake Ecosystem (Brokers, Banks, Retail Traders, Institutional Traders)
3.8. Porters Five Forces (Bargaining Power of Buyers, Suppliers, Competitive Rivalry, Threat of Substitutes, New Entrants)
3.9. Competition Ecosystem
4. Global ForEx Market Segmentation
4.1. By Transaction Type (In Value %)
4.1.1. Spot Transactions
4.1.2. Forward Transactions
4.1.3. Swap Transactions
4.1.4. Options Transactions
4.2. By Participant Type (In Value %)
4.2.1. Commercial Banks
4.2.2. Central Banks
4.2.3. Hedge Funds
4.2.4. Retail Traders
4.3. By Currency Pair Type (In Value %)
4.3.1. Major Currency Pairs (USD/EUR, USD/JPY)
4.3.2. Minor Currency Pairs (EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD)
4.3.3. Exotic Currency Pairs (USD/BRL, EUR/ZAR)
4.4. By Trading Platform (In Value %)
4.4.1. Traditional Bank Platforms
4.4.2. Online Brokers
4.4.3. Mobile Trading Apps
4.5. By Region (In Value %)
4.5.1. North America
4.5.2. Europe
4.5.3. Asia-Pacific
4.5.4. Middle East & Africa
4.5.5. Latin America
5. Global ForEx Market Competitive Analysis
5.1. Detailed Profiles of Major Competitors
5.1.1. JPMorgan Chase
5.1.2. Deutsche Bank
5.1.3. Citibank
5.1.4. UBS Group
5.1.5. Barclays
5.1.6. XTX Markets
5.1.7. BNP Paribas
5.1.8. HSBC
5.1.9. Goldman Sachs
5.1.10. Bank of America Merrill Lynch
5.1.11. Morgan Stanley
5.1.12. State Street Corporation
5.1.13. EBS (Electronic Broking Services)
5.1.14. Refinitiv
5.1.15. Saxo Bank
5.2. Cross Comparison Parameters (Number of Employees, Headquarters, Trading Volume, Inception Year, Currency Pairs Offered, Trading Platforms, Technology Adoption, Revenue)
5.3. Market Share Analysis
5.4. Strategic Initiatives
5.5. Mergers And Acquisitions
5.6. Investment Analysis
5.7. Venture Capital Funding
5.8. Government Grants
5.9. Private Equity Investments
6. Global ForEx Market Regulatory Framework
6.1. Market Infrastructure Regulation (BIS Reporting Standards, ISDA Agreements)
6.2. Compliance Requirements (MiFID II, Dodd-Frank Act)
6.3. Certification Processes (Trader Certifications, Platform Security Audits)
7. Global ForEx Future Market Size (In USD Trillion)
7.1. Future Market Size Projections
7.2. Key Factors Driving Future Market Growth
8. Global ForEx Market Future Segmentation
8.1. By Transaction Type (In Value %)
8.2. By Participant Type (In Value %)
8.3. By Currency Pair Type (In Value %)
8.4. By Trading Platform (In Value %)
8.5. By Region (In Value %)
9. Global ForEx Market Analyst Recommendations
9.1. TAM/SAM/SOM Analysis
9.2. Customer Cohort Analysis
9.3. Marketing Initiatives
9.4. White Space Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involved identifying key variables influencing the global ForEx market, such as transaction volumes, liquidity levels, and regulatory frameworks. This phase was supported by desk research and analysis of government publications, including data from the Bank for International Settlements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data analysis of trading volumes and currency pair performance was conducted to establish market trends. This involved reviewing data from trading platforms and major financial institutions to construct a reliable market framework.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Expert consultations were conducted with market participants, including senior analysts from banks and hedge funds. These insights provided validation for the trading volumes, liquidity trends, and the rise of algorithmic trading within the ForEx market.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final stage of the research involved synthesizing all collected data and insights into a comprehensive analysis of the global ForEx market. The output was cross-verified with data from proprietary databases and third-party financial institutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. How big is the Global ForEx Market?
The global ForEx market is valued at over USD 800 billion in daily trading volume. This massive market size is driven by the need for currency exchanges in international trade and investment, with both institutional and retail traders actively participating.
02. What are the challenges in the Global ForEx Market?
Key challenges in the ForEx market include heightened regulatory scrutiny, currency volatility due to geopolitical events, and cybersecurity risks associated with digital trading platforms. These factors can lead to operational disruptions and increased compliance costs.
03. Who are the major players in the Global ForEx Market?
Major players include JPMorgan Chase, Citibank, Deutsche Bank, UBS Group, and HSBC. These companies dominate the market through their vast networks, advanced trading platforms, and high liquidity in major currency pairs.
04. What are the growth drivers of the Global ForEx Market?
The ForEx market is driven by factors such as technological advancements in trading platforms, the expansion of international trade, and increasing retail trader participation. The rise of mobile and algorithmic trading is also contributing to market growth.
Why Buy From Us?

What makes us stand out is that our consultants follows Robust, Refine and Result (RRR) methodology. i.e. Robust for clear definitions, approaches and sanity checking, Refine for differentiating respondents facts and opinions and Result for presenting data with story

We have set a benchmark in the industry by offering our clients with syndicated and customized market research reports featuring coverage of entire market as well as meticulous research and analyst insights.

While we don't replace traditional research, we flip the method upside down. Our dual approach of Top Bottom & Bottom Top ensures quality deliverable by not just verifying company fundamentals but also looking at the sector and macroeconomic factors.

With one step in the future, our research team constantly tries to show you the bigger picture. We help with some of the tough questions you may encounter along the way: How is the industry positioned? Best marketing channel? KPI's of competitors? By aligning every element, we help maximize success.

Our report gives you instant access to the answers and sources that other companies might choose to hide. We elaborate each steps of research methodology we have used and showcase you the sample size to earn your trust.

If you need any support, we are here! We pride ourselves on universe strength, data quality, and quick, friendly, and professional service.















