International Remittance Industry in Qatar: Outlook to 2025
Region:Middle East
Author(s):Lakshay Aggarwal
Product Code:KR1101
November 2021
20
About the Report
The publication titled ‘International Remittance Industry in Qatar’ covers the overview of industry by analyzing historical remittance statistics and corresponding change in social-demographic indicators in Qatar. With ~88% of expat population, the value of outbound remittance transactions were recorded at QAR XX Bn in 2020, down from QAR XX Bn in 2019 due to COVID-19 restrictions and return of expat population to home countries. Given the dominance of local exchange houses, analysts have elaborated on competitive landscape of major exchange houses on the basis of operational and financial parameters, highlighted growth drivers and risk factors governing the future outlook of industry.
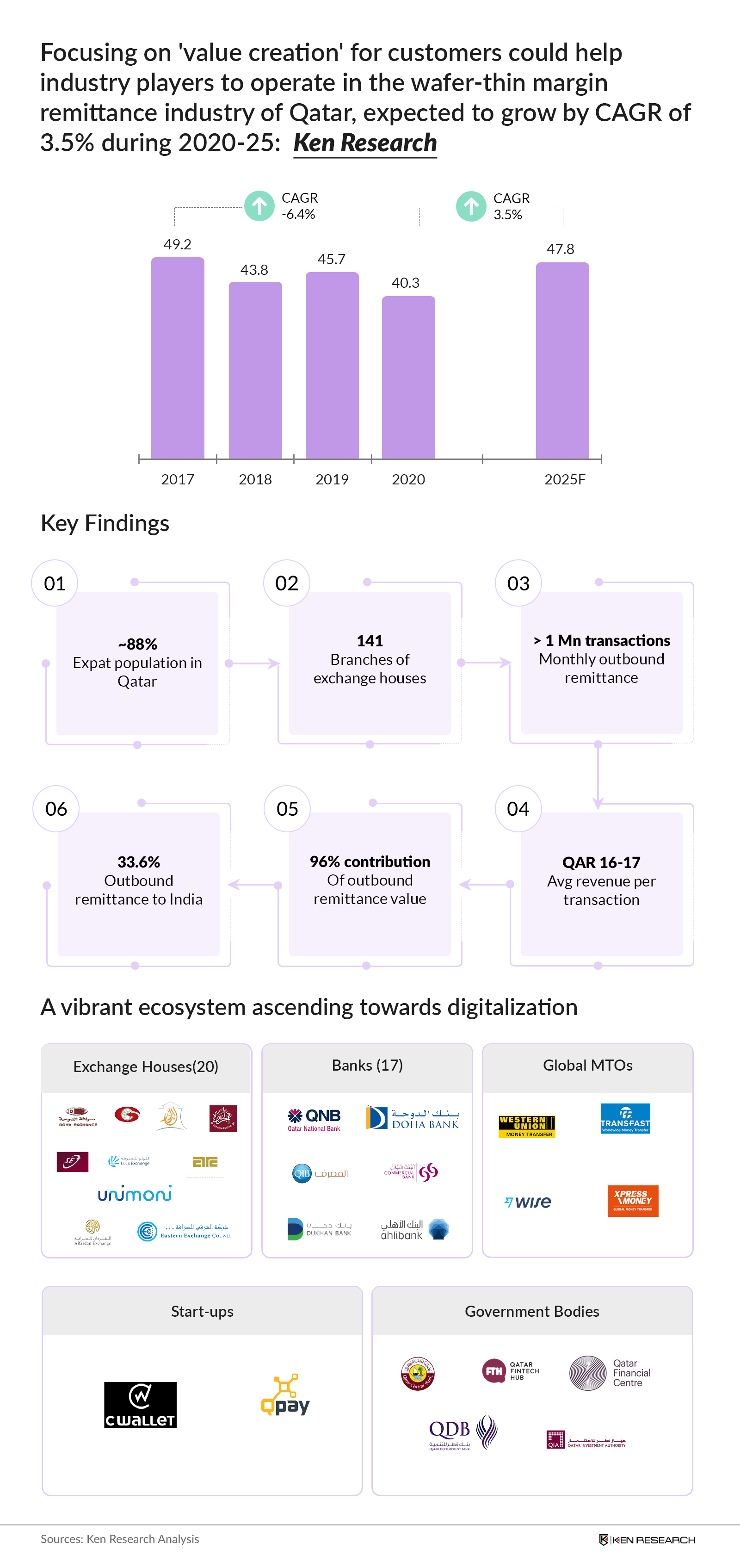
Overview of Industry: The growth in expat population from XX Mn in 2010 to XX Mn in 2019 and increased share of remitted money as a proportion of salary have contributed to the increased value of remittance transactions in Qatar from QAR XX Bn in 2016 to QAR XX Bn in 2019. While, India remains the largest outbound remittance corridor, there has been tremendous growth in outbound remittance to Bangladesh with its contribution surging from XX% in 2016 to XX% in 2020. As at June 2021, there were XX local exchange houses operating via XX branches across Qatar. Al Dar for exchange works operated the highest number of XX branches in Doha, Ar Rayyan, Al Khor etc.
Drivers and Impediments to growth: In line with the National Vision 2030 and upcoming FIFA World Cup event in 2022, remittance industry in Qatar has been witnessing introduction and adoption of digital solutions (Web and mobile application) by migrant population. The pandemic of COVID-19 compelled workers to return to their home countries while lockdown on exchange houses forced users to switch to online mediums for transactions. Further, the restrictions on daily transfer limit and corresponding daily funding issues in certain small exchange houses had led to shift of high value customers to leading players.
A push by Qatari Government to promote Fintech
Qatar Central Bank (QCB) has played a crucial role in promoting and regulating the industry with vigilance on compliance with Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Financing of Terrorism. Further, partnership of QCB with Qatar Development Bank and Qatar Financial Center to launch Qatar Fintech Hub has provided for incentives (waiver of application fees and first year registration fees, rent free workspaces, 100% foreign ownership and repatriation of profits etc.) aim to encourage investments in startups in Qatar. In a whitepaper released in October 2021, the stakeholders have highlighted the role of technology and its surging adoption which could pave way for Qatar as a regional hub for Fintech.
A Vibrant Future Outlook:
Given the backdrop of decrease in volume and value of outbound international remittance transactions, analysts at Ken Research expect a growth of XX% during 2020-21 and CAGR of XX% during 2020-25F. During this period, value of transactions is expected to peak in 2022 owing to arrival of more than XX Million foreign travelers for FIFA World Cup 2022 event. It is also expected that industry would witness increased level of partnerships among banks, exchange houses and financial services entities aiming to gaining ownership in value chain.
While, digitalization of services coupled with wafer-thin operating margins are here to stay for tomorrow, it is pertinent for incumbents to re-assess their business strategy and focus on creating value for customers of tomorrow.
Key Topics Covered in the Report
- Overview of International Remittance Industry in Qatar (Statistics on Corridor wise Transaction volume and value)
- Industry segmentation (By Type of Transfers, Type of Intermediary Operators, Corridor wise, Type of Source Entities)
- Cross Comparison of Major Exchange houses on Operational and Financial Parameters (December 2020, June 2021)
- Company Profile of Major Exchange Houses (Overview, Products and Services, USP, Business Strategies, Branch wise Operational Performance, Cumulative Financial Performance, Recent Developments)
- Growth Drivers and Challenges to Qatar International Remittance Industry
- Industry trends and developments
- Rules and Regulations by Government Bodies
- Impact of COVID-19 and Future Outlook of Industry
Products
Table of Contents
1. Overview of International Remittance Industry of Qatar
1.1. Market size of Industry basis Value of Transactions, QAR Mn (2016-20)
1.2. Market segmentation basis Type of Flows (Inbound and Outbound)
1.3. Market segmentation of Outbound Remittance transaction value basis Corridor (India, Nepal,
Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Philippines, Egypt and others)
1.4. Market size of Outbound Remittance basis average volume of monthly transactions in Million
during 2016-20
1.5. Market size of Outbound Remittance basis industry revenue in QAR Mn during 2016-20
1.6. Market segmentation of Outbound Remittance transaction value basis Type of Source Entity
(Banks, Exchange Houses)
1.7. Market segmentation of Outbound Remittance transaction value basis Type of Intermediary
Operators (Correspondent Banking Networks, Third Party Operators)
1.8. Market segmentation of Outbound Remittance transaction value basis Type of Transfers
(Direct to Account, Cash Pickup)
2. Trends and Developments in International Remittance Industry of Qatar
2.1. Qatar National Vision 2030, National Fintech Strategy
2.2. Digitalization, Pricing Trends
3. Rules and Regulations in International Remittance Industry of Qatar
3.1. For opening new Branches
3.2. Procedure, Registration and Fees for exchange houses
3.3. Compliance with AML guidelines and recent regulations
4. Competitive Landscape of International Remittance Industry of Qatar
4.1. Competition scenario between Banks and Exchange Houses
4.2. Year of Establishment, Branches in Qatar and Digital Solution offering of banks and
exchange houses
4.3. Cross-Comparison among top exchange houses basis:
4.3.1. Volume of monthly Outbound Remittance Transactions (December 2020, June 2021)
4.3.2. Market share basis volume of monthly Outbound Remittance Transactions (December 2020,
June 2021)
4.3.3. Annual Value of Outbound Remittance Transactions in QAR Mn (December 2020, June 2021)
4.3.4. Market share basis Annual Value of Outbound Remittance Transactions in Percentage
(December 2020, June 2021)
4.3.5. Market share basis number of branches in Qatar, June 2021
4.3.6. Market share basis revenue from outbound remittance transactions in Percentage, 2020
4.3.7. Average Outbound Transaction size, 2020
4.3.8. Corridor wise value of outbound transaction in QAR Mn
4.3.9. Market share basis corridor wise value of outbound transaction in Percentage, 2020
5. Company Profiles of Top Exchange Houses on parameters – Company Overview, Products and
services offered, USP, Partnerships, Branch-wise Operational Performance, Financial
Performance, Impact of COVID-19 on Business
5.1. Al Dar for Exchange Works
5.2. Al Fardan Exchange
5.3. Al Jazeera Exchange
5.4. Unimoni Exchange
5.5. Gulf Exchange
5.6. Doha Exchange
5.7. Al Mana Exchange
5.8. Habib Qatar International Exchange
5.9. Travelex
6. Porter 5 Forces analysis
7. Risk Factors governing International remittance industry of Qatar
7.1. Recent Funding Issues, Homogenous offerings, Wafer-thin margins
8. Impact of COVID-19 and Future Outlook of Industry
8.1. Evaluation of operational performance of Exchange Houses
8.2. Future market size basis value of international remittance transactions in QAR Mn, 2020-
25F
8.3. Future market size basis revenue from outbound international remittance transactions in
QAR Mn, 2020-25F
8.4. Future Market segmentation of Outbound Remittance transaction value basis Corridor (India,
Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Philippines, Egypt and others), 2025F
8.5. Future Market segmentation of Outbound Remittance transaction value basis Type of Source
Entity (Banks, Exchange Houses), 2025F
9. Research Methodology
9.1. Definitions
9.2. Research Methodology
9.3. Research Limitations
Disclaimer
Why Buy From Us?

What makes us stand out is that our consultants follows Robust, Refine and Result (RRR) methodology. i.e. Robust for clear definitions, approaches and sanity checking, Refine for differentiating respondents facts and opinions and Result for presenting data with story

We have set a benchmark in the industry by offering our clients with syndicated and customized market research reports featuring coverage of entire market as well as meticulous research and analyst insights.

While we don't replace traditional research, we flip the method upside down. Our dual approach of Top Bottom & Bottom Top ensures quality deliverable by not just verifying company fundamentals but also looking at the sector and macroeconomic factors.

With one step in the future, our research team constantly tries to show you the bigger picture. We help with some of the tough questions you may encounter along the way: How is the industry positioned? Best marketing channel? KPI's of competitors? By aligning every element, we help maximize success.

Our report gives you instant access to the answers and sources that other companies might choose to hide. We elaborate each steps of research methodology we have used and showcase you the sample size to earn your trust.

If you need any support, we are here! We pride ourselves on universe strength, data quality, and quick, friendly, and professional service.















